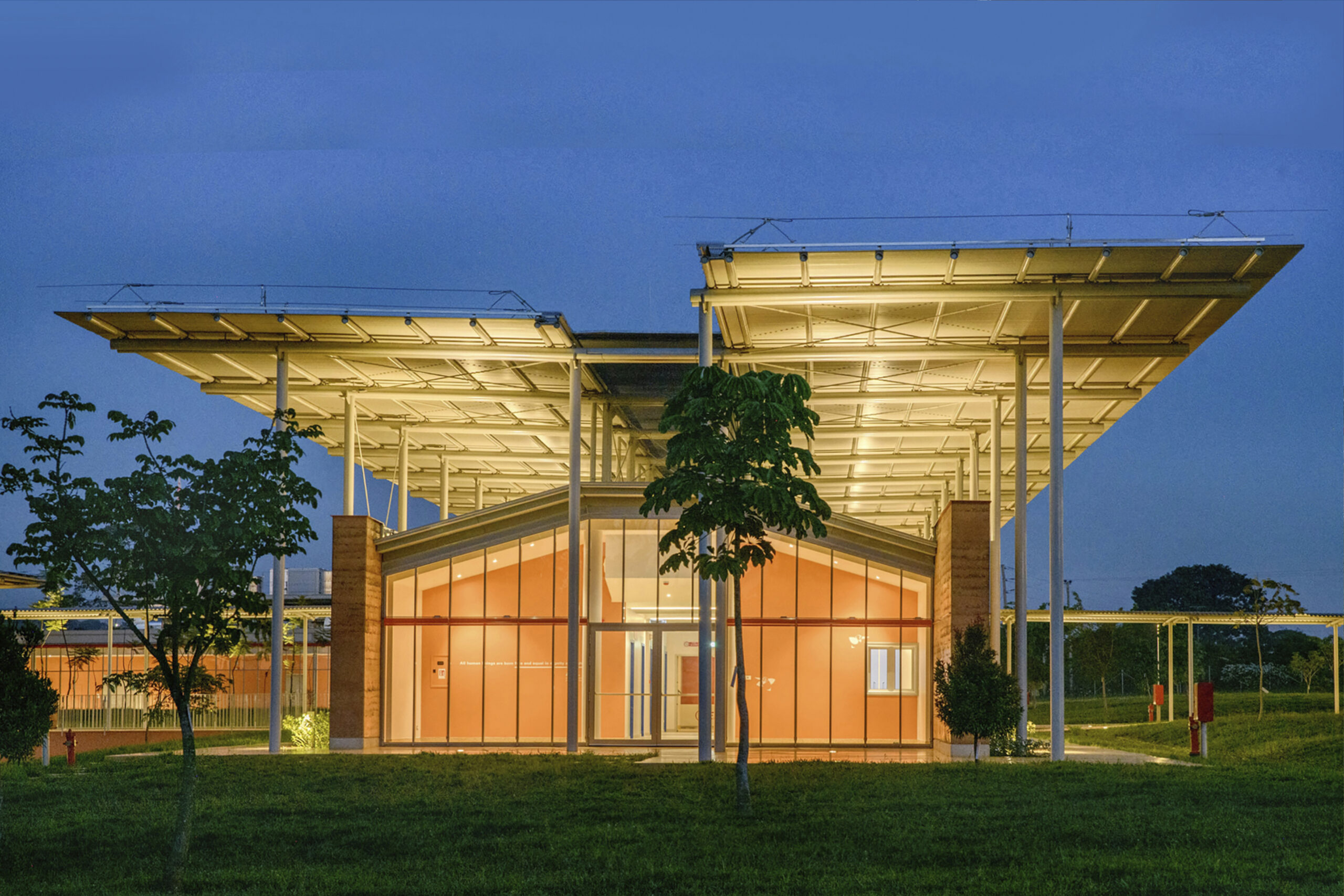

Stavros Niarchos Foundation, a philanthropic organization that funds projects in the fields of art, culture, education, health and social welfare, has commissioned Arch. Renzo Piano to design three new facilities for the Hellenic Republic's national health system. Following a memorandum of understanding signed with the Greek government, the health system will thus be implemented through three facilities built with very high criteria of efficiency, sustainability and innovation: two general hospitals, in Komotini and Sparta, and a new university children's hospital, in Thessaloniki.
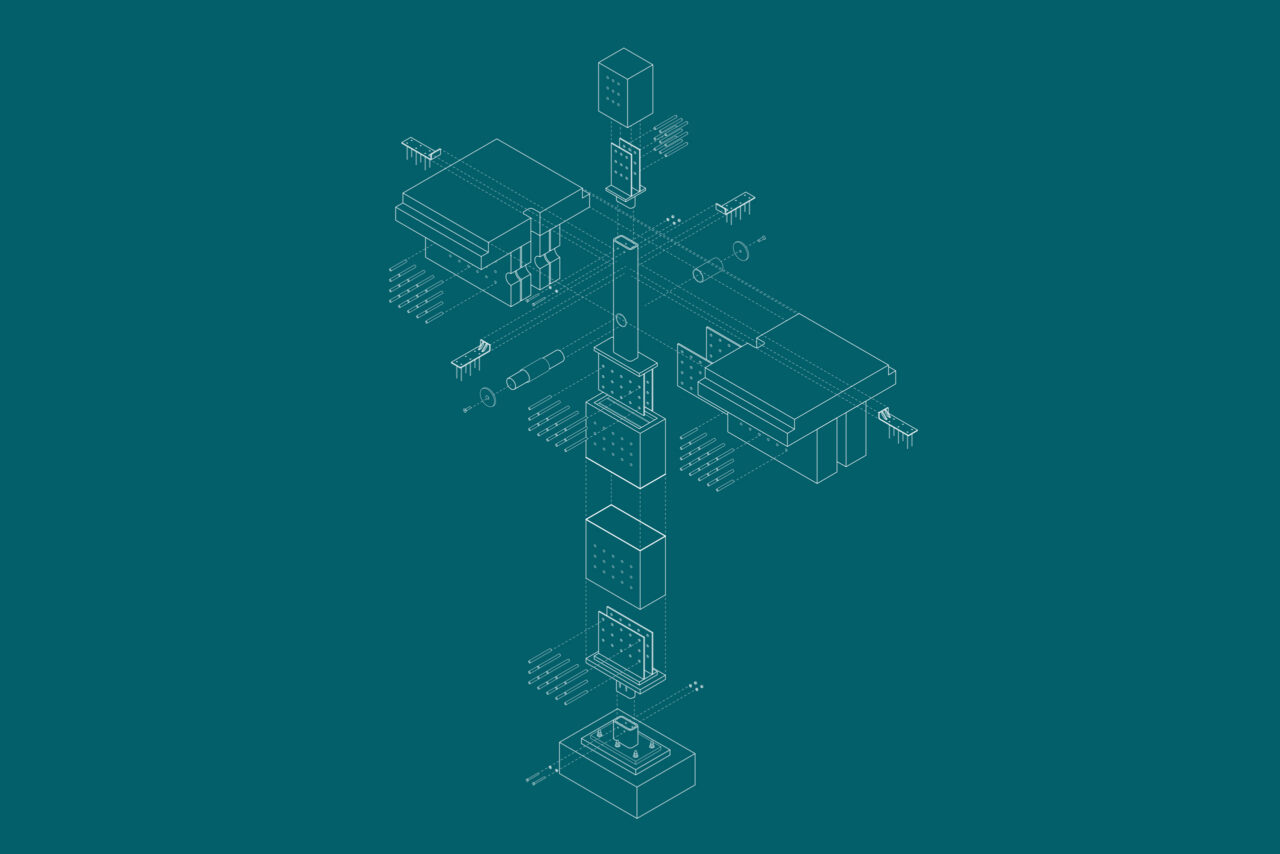
A number of common principles guided the design of the three complexes, beginning with the centrality accorded to the individual and the attention paid to the natural context in which they will be integrated. The three facilities will be immersed in environments that, in addition to allowing users to benefit from the therapeutic properties of nature, will also allow optimal use of natural light and ventilation in all areas of the buildings. Architecturally, the designs of the three hospitals are united by the presence of wooden structures, glulam columns and beams supporting X-Lam floors.
The intervention will allow the decommissioning of the city's old hospital, among the oldest in the country, creating in its place a modern facility according to the highest criteria of efficiency and sustainability for the benefit of the inhabitants of the region of East Macedonia and Thrace. Three basic concepts guided the project: high seismic resistance, durability, and sustainability. In relation to the latter, the complex will have access to energy produced by 30 km of geothermal wells, which, together with the photovoltaic canopy shading the structure, will fully meet the building's heating and cooling needs. Structurally, the ground floor of Komotini General Hospital will be made of concrete, while the first and second floors will be built of wood, with glulam columns and beams supporting cross-laminated timber (CLT) floors.
Among the elements that the three hospitals designed by Arch. Renzo Piano for the Stavros Niarchos Foundation have in common is their attention to the natural environment in which they are located and integrated: a detail that translates first and foremost into the careful use of renewable energy resources and respect for the principles of energy and social sustainability. The use of natural light and ventilation, for example, finds application both in public spaces and in inpatient rooms. Moreover, as in the Asklepeion, the healing temple of ancient Greece, this triple intervention also places nature in a therapeutic role in the patient's rehabilitation process.
From a technological point of view, the three basic parameters that were observed during the design are high seismic resistance, durability and sustainability. In this regard, the use of wood as a building material for above-ground structures is functional in meeting all three, as it is a strong, durable and above all lightweight material - a fundamental property for an earthquake-resistant structure. The construction system is made of glulam pillars and double beams, to which walkable decks made of X-lam panels are applied. In the event of a seismic event, rigidity and sound insulation are provided by a concrete hood cast over the floors.
info@buromilan.com
stampa@buromilan.com
C.F./P.I. 08122220968
C.D. M5UXCR1
Via Thaon di Revel, 21
20159 Milan - Italy
T +39 02 36798890
Santa Croce 458/A
30135 Venice - Italy
T +39 041 5200158